

Knowing the different tools and technologies available is essential for professionals working with the internet. HTML is a key area of knowledge for those looking to pursue this career path.
HTML, which predates the modern internet, is found on various online platforms and has continued to evolve over time.
Discover in this article what HTML is and how this language functions, as well as where and how to learn it for free to become proficient in the topic.
Contents.
- What does HTML stand for?
- How it operates and the HTML attributes of HTML elements.
- Attributes of HTML tags
- Most commonly used HTML elements
- Using HTML in everyday situations
- HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- HTML5 is a contemporary iteration of HTML.
- Where can one acquire skills in HTML?
- Conclusion
- HTML tag properties
What is HTML?
HTML is like the building block of a web page, hidden from view but essential for structuring the content.
The term HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language, referring to a language used for creating text with links that allow users to navigate freely, similar to our online browsing experience.
HTML is utilized for organizing a webpage, while CSS is responsible for its visual presentation. Further details on CSS will be provided later.
What is a website, how it functions, and its significance in a business are also worth considering.
How it functions and the purpose of HTML
HTML is a markup language that marks and adds significance to information on a webpage, where the tags are interpreted by the browser to identify various elements like titles, paragraphs, images, and lists.
An HTML tag consists of a less than sign and a greater than sign, like
and
, respectively, in the following way:
Some tags, such as the img element, do not require closure and are known as orphan tags or empty elements.
The tag doesn’t directly add the image to the page; instead, it designates a space for the image linked through the src attribute.
HTML is crucial not only for browsers but also for search engines like Google and Bing. It allows search engines to analyze and categorize webpage content, with bots using automated scripts to scan and index information efficiently.
HTML tag attributes are elements used in HTML to provide additional information about an element.
An HTML element may have attributes, which provide additional information to the element.
The tag requires the src attribute to display an image on the page, as it specifies the path to the image file. Without a valid link in the src attribute, no image will be shown.
The alt attribute in the image tag is crucial as it provides alternative text for the image, benefiting visually impaired users, SEO practices, and instances where the image cannot be displayed.
Another commonly used tag is the tag, which is utilized for generating page links. A link requires a destination address, established through the href attribute. Here is an example of how to insert a link on a page using HTML markup:
When the browser reads the markup above, it will show just the link, such as “access Google here.”
Most commonly used HTML elements
There are more than 100 valid tags in the most recent HTML version, but some are commonly found on nearly all HTML pages. Let’s take a look at a few of them.
HTML tags for organizing page or document structure.
| Tag | Usage |
|
Document Specification |
|
HTML document root |
|
Page header |
|
Meta information (e.g. page language) |
|
Page title (do not confuse with text titles, e.g.: h1) |
|
Body (where the page’s visible content goes) |
|
Styles (appearance) |
|
Navigation (used for menus) |
|
Article (delimits the content of an article) |
|
Division |
Tags for marking text:
| Tag | Usage |
|
Titles |
|
Paragraph |
e |
Italics |
e |
Negative |
|
Link |
|
Unordered list |
|
Ordered list |
|
Element of a list |
|
Quotation |
|
Horizontal line |
|
Image |
To illustrate the mentioned tags, a webpage with a basic layout might include the following labeling:
Try pasting the provided code into a simple text editor like Notepad. Save the file with a .html extension (e.g., page.html) and then open it to view a basic HTML page in your browser. Avoid using rich text editors like Word or Google Docs as they are not suitable for editing HTML.

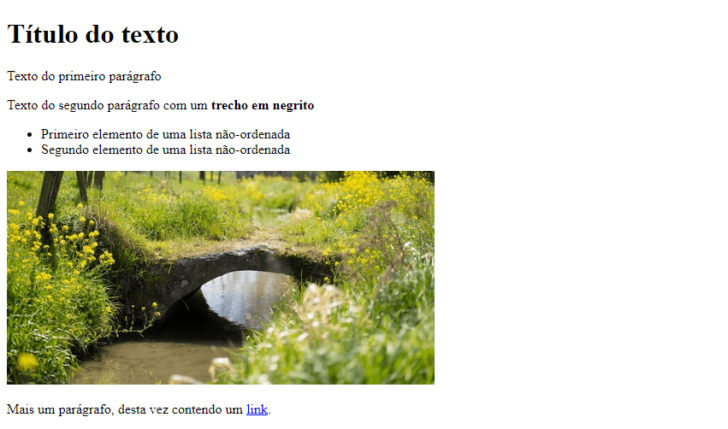
For a complete list of HTML tags, refer to this webpage from the Mozilla Foundation.
HTML utilization in everyday life
In a recent code example I showed, we created a complete HTML page. In the early days of the internet, this was the sole method for website creation, requiring manual HTML coding. Fortunately, this process has evolved.
Several tools and platforms are available to simplify the process of generating HTML codes and other necessary languages for a webpage, reducing the workload for web developers.
Having a grasp of HTML can be both intriguing and essential for individuals working in digital environments, particularly in content creation fields. Major publishing platforms like WordPress and Wix now support the utilization and modification of HTML within your pages.

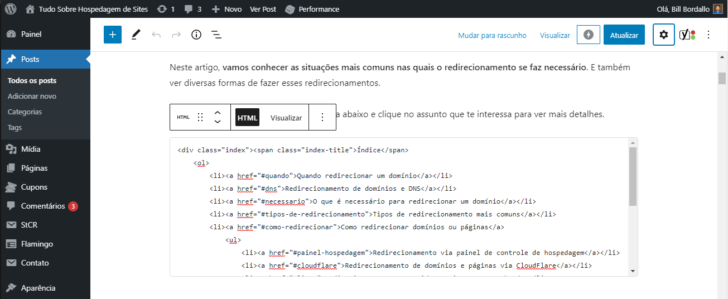
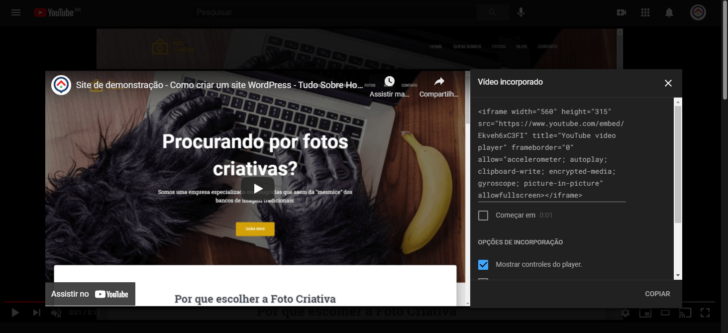
It is often essential to work with HTML code insert, regardless of the platform used, when going beyond basic text formatting. For instance, incorporating a YouTube video on your website requires using the iframe tag from the platform. The same applies to adding social media sharing buttons, which offer ready-to-use HTML codes. To monitor your website’s audience, Google Analytics typically provides an HTML code snippet for inserting across all pages.

chsyys/Flickr
HTML, CSS and Javascript are coding languages.
HTML is not the sole language on a webpage; other languages like CSS and Javascript are utilized to enhance user content and experience on the browser.
CSS is a specialized language for enhancing the visual design of a webpage. It can be applied within the HTML file or sourced externally. The syntax of CSS varies significantly from HTML as it involves grouping style declarations. This allows for uniform styling adjustments across multiple elements using a single rule in the CSS file linked to the HTML document.

Javascript is a programming language that can change behavior and execute different tasks on a webpage. It can be incorporated in an HTML file directly or linked externally using the script tag. Javascript enables interactions that are essential for the functionality of the internet, such as hiding/showing menus, creating image carousels, and validating form data.
A contemporary edition of HTML is HTML5.
The British physicist Tim Berners-Lee created the HTML language to make it easier for him and his colleagues to communicate and share scientific work. The language’s simplicity contributed to its rapid adoption for use on the emerging public internet, which later evolved into the internet we know today.
The original HTML was introduced in 1991 and underwent various improvements before HTML 4.01 was released in 1999, adapting to the evolving internet landscape.
In 2014, the latest version of HTML, known as HTML5, was launched. This update included enhancements to the language, including new tags like


